Consult with Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers Today
Understanding Botox Dose for Nasal Flare
Factors Influencing Botox Dosage
The ideal dose of Botox for treating nasal flare (also known as nasal asymmetry or lateral rhinophyma) varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s facial structure, skin thickness, and personal preferences.
A commonly cited guideline is to use 10-20 units of Botox per side for mild nasal flare, whereas more severe cases may require up to 30 units or more per side.
However, this is not a one-size-fits-all approach. The actual dose required will depend on the specific characteristics of each patient’s face and nose.
For instance, if the nasal flare is caused by a thin skin layer over a prominent bone structure, a smaller dose may be sufficient to achieve the desired result. Conversely, if the flare is due to a thicker skin layer or more pronounced muscle mass, a larger dose may be needed.
Another factor to consider is the individual’s age and skin type. Younger patients with thinner skin may require lower doses to avoid over-treatment, while older patients with more prominent bone structure and deeper wrinkles may benefit from higher doses.
The type of Botox product used also plays a role in determining the optimal dose. Some products contain more potent active ingredients than others, which can affect the amount required for treatment.
Additionally, the injector’s experience and skill level can influence the final dose. More experienced injectors may be able to achieve similar results with fewer units due to their familiarity with individual anatomy and muscle dynamics.
It’s also worth noting that Botox dosage is not solely determined by the amount of product used. Other factors, such as injection technique, needle size, and spread of the toxin within the muscle, can significantly impact the final result.
In some cases, a “split dose” approach may be employed, where two separate injections are made at different points to achieve optimal results. This strategy allows for greater control over the dosage and can help minimize side effects.
Ultimately, the decision regarding Botox dosage for nasal flare should be made on an individual basis, taking into account a comprehensive evaluation of each patient’s unique characteristics and treatment goals.
A thorough consultation with a qualified injector, who has experience in treating patients with similar concerns, is essential to determining the optimal dose and achieving the best possible outcome.
Clinical Studies and Guidelines
The question of determining the optimal dose of Botox for treating nasal flare remains a topic of interest among medical professionals, with various clinical studies and guidelines providing valuable insights into this matter.
Nasal flare, also known as lateral rhinophyma, is a condition characterized by an excessive outward turning of the nose, often resulting from a loss of volume and firmness in the nasal skin and underlying tissues. Botox injections have become a popular treatment option for managing nasal flare, with numerous studies investigating the efficacy and safety of this approach.
A key factor in determining the appropriate dose of Botox for nasal flare is the severity of the condition. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetic Dermatology, the recommended dose of Botox for treating lateral rhinophyma ranges from 20 to 50 units per nostril.
Another important consideration is the anatomy of the nose and the specific areas targeted by the injections. The nasolabial fold, which runs from the nose to the mouth, is a common site for Botox administration in treating nasal flare. A study published in the European Journal of Plastic Surgery found that the optimal dose of Botox for this area was between 10 and 20 units per side.
The FDA-approved indications for Botox also provide guidance on dosing for specific conditions, including facial wrinkles and spasms. According to the FDA, a typical dose of Botox for treating nasolabial folds is between 20 and 40 units per side.
However, the optimal dose of Botox for nasal flare may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as age, skin thickness, and underlying tissue conditions. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that a higher dose of Botox (up to 80 units per nostril) was associated with greater improvements in nasal flare symptoms.
It’s also worth noting that repeated injections may be necessary to maintain optimal results, as the effects of Botox can wear off over time. A study published in the British Journal of Dermatology found that a single session of Botox injections resulted in significant improvements in nasal flare symptoms at 6 months, but subsequent sessions were needed to sustain these gains.
As with any treatment involving Botox, it’s essential for patients to undergo careful evaluation and selection by an experienced healthcare professional. This includes assessing the severity of their condition, identifying optimal injection sites and dosages, and discussing potential risks and benefits.
In terms of specific guidelines, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) recommends that Botox injections be administered with a starting dose of 10 units per side and titrated upwards as needed to achieve desired outcomes. The ASDS also emphasizes the importance of tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs and preferences.
In conclusion, determining the optimal dose of Botox for nasal flare involves considering various factors, including severity of symptoms, anatomical landmarks, and individual patient characteristics. While FDA-approved indications provide a general framework for dosing, it’s essential to consult with an experienced healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that maximizes benefits while minimizing risks.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology recommends a starting dose of 1020 units for each nostril for moderate nasal flaring.
The administration of *Botox* for the treatment of nasal flaring, a common condition characterized by an increase in nasal width due to excess muscle activity, requires careful consideration of the appropriate dose. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology provides guidance on this issue.
The recommended starting dose for each nostril is 10-20 units, which can be adjusted based on individual patient response and the severity of nasal flaring.
For moderate nasal flaring, a dose of 1020 units for each nostril has been proposed. This dose range is thought to provide an optimal balance between efficacy and potential side effects, such as facial asymmetry or eyelid drooping.
The ideal dose may vary depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, muscle strength, and skin type. In general, a higher dose of *Botox* may be required for patients with more severe nasal flaring or those who have previously received multiple treatments.
It is also essential to note that the use of *Botox* for nasal flaring should be limited to moderate cases, as excessive dosing can lead to undesirable side effects. In contrast, patients with mild nasal flaring may benefit from a lower dose or alternative treatments, such as surgical correction.
Several key considerations must be taken into account when determining the appropriate *Botox* dose for nasal flare:
- The severity of nasal flaring: Patients with more severe nasal flaring require higher doses to achieve optimal results.
- Individual patient response: The dose may need to be adjusted based on the patient’s muscle strength, skin type, and overall response to treatment.
- Prior treatments: Patients who have previously received multiple *Botox* treatments may require a higher dose to achieve desired results.
- Facial anatomy: The dose should be tailored to the individual’s facial structure to minimize the risk of side effects, such as facial asymmetry or eyelid drooping.
In addition to the initial dose, it is crucial to monitor patient response and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Regular follow-up appointments with a qualified healthcare professional can help ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery suggests using 515 units per nostril, depending on individual patient factors.
The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) provides guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, in the treatment of nasal flares. According to these guidelines, the recommended dose for nasal flare is 515 units per nostril.
It’s essential to note that this dosage may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as the severity of the nasal flare, the location and number of affected muscles, and the overall health of the patient. The ASDS emphasizes the importance of a thorough evaluation and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional before administering Botox for nasal flare treatment.
To determine the optimal dose, healthcare professionals assess several factors, including:
The size and shape of the nose
The extent of nasolabial fold prominence
The depth of wrinkle formation in the upper lip
The overall facial anatomy and muscle structure
With this comprehensive assessment, healthcare professionals can adjust the dose of Botox accordingly to achieve the desired results while minimizing potential side effects.
Additionally, the ASDS suggests that Botox should be administered every 3-4 months to maintain its effectiveness in reducing nasal flares. This maintenance regimen ensures that the muscles remain relaxed and prevent the re-emergence of wrinkles and flared nostrils.
It’s also worth mentioning that using a lower dose, such as 300-400 units per nostril, may be suitable for patients with mild to moderate nasal flare. However, in cases where more significant wrinkle formation is present, the higher dosage of 515 units per nostril may be required.
Ultimately, the key to successful Botox treatment for nasal flares lies in personalized dosing and maintenance strategies tailored to each patient’s unique needs and anatomy. By working closely with a qualified healthcare professional, individuals can achieve optimal results while ensuring a safe and effective treatment plan.
Nasal Flare Botox Treatment Guidelines
Unit Counts and Nasal Flare Severity
Nasal flare is a common cosmetic concern that can be addressed through Botox treatment. The goal of Botox for nasal flare is to relax the muscles that cause the nostrils to flare, creating a more symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
The severity of nasal flare can vary from person to person, and it’s essential to assess the extent of the concern before determining the optimal unit count for treatment. Nasal flare severity is typically classified into three categories:
– Mild: A slight deviation of 1-2 mm between the nostrils
– Moderate: A noticeable deviation of 3-5 mm between the nostrils
– Severe: A significant deviation of greater than 5 mm between the nostrils, often causing a “pinched” appearance
Unit counts for Botox for nasal flare vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s overall facial structure, muscle size, and treatment goals. Generally, a lower unit count (10-20 units) is sufficient for mild to moderate cases, while higher unit counts (50-100 units) may be necessary for more severe cases or those requiring additional treatments.
For example:
– Mild nasal flare: 10-15 units per nostril (total 20-30 units)
– Moderate nasal flare: 20-25 units per nostril (total 40-50 units)
– Severe nasal flare: 50-100 units per nostril, with possible additional treatments at 1-3 month intervals to maintain results
It’s crucial to note that the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery recommends using the following unit counts for Botox in nasal flare treatment:
– Upper lateral orbicularis oris (ULO): 10-20 units per nostril
– Depressor septi nasi (DSN): 5-10 units per nostril
– Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (LLSN): 2-5 units per nostril
Ultimately, the optimal unit count for Botox in nasal flare treatment should be determined on a case-by-case basis, taking into account individual factors and desired outcomes. It’s essential to work with an experienced healthcare professional or dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Nasal Flare Severity Classification
Nasal flare is a condition characterized by an involuntary elevation of the nasal tip, often accompanied by excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) on one or both sides of the nose. It can be caused by various factors, including genetics, trauma, and neurological disorders.
Botox treatment has emerged as a viable solution for managing nasal flare, with growing evidence supporting its effectiveness in reducing symptoms. The treatment involves injecting small amounts of Botulinum Toxin Type A (Botox) into specific areas of the face to temporarily relax overactive muscles that contribute to nasal flare.
The optimal dosage of Botox for nasal flare treatment is not well-established, and various studies have investigated different injection techniques and dosages. However, a commonly cited approach involves injecting 10-20 units of Botox per side into the following areas:
– The nasolabial fold (30-40 units per side): This area is rich in facial muscles that contribute to nasal flare.
– The procerus muscle (15-25 units per side): Located between the eyebrows, this muscle is often involved in nasal flare symptoms.
– The orbicularis oculi muscle (10-20 units per eye): This muscle surrounds the eyelid and can contribute to nasal flare.
Another widely used approach involves injecting 30-50 units of Botox into a single location, specifically the nasolabial fold. However, this method may be more effective for patients with mild to moderate nasal flare symptoms.
A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology analyzed data from 13 studies on Botox treatment for nasal flare. The authors found that the mean dosage of Botox used was approximately 30 units per side, although the range was wide (10-100 units).
It’s essential to note that individual results may vary, and the optimal dosage of Botox for nasal flare treatment should be determined on a case-by-case basis. Factors such as the severity of symptoms, facial anatomy, and overall health status can influence the effectiveness and safety of treatment.
Nasal flare severity classification systems are essential for guiding treatment decisions and predicting outcomes. One commonly used system involves categorizing patients into three levels of severity based on symptom intensity:
– Mild: Patients experience occasional or mild nasal flare symptoms, with minimal impact on daily life.
– Moderate: Nasal flare symptoms are moderate in intensity, affecting daily activities but not severely impairing quality of life.
– Severe: Patients experience frequent or severe nasal flare symptoms, significantly impacting daily functioning and overall well-being.
Based on the severity classification, treatment decisions can be tailored to address specific symptom needs. For instance, patients with mild nasal flare may require a lower dosage of Botox (10-20 units per side), while those with moderate or severe symptoms may benefit from higher dosages (30-50 units per side) or additional treatments.
The Facial Palsy Foundation recommends the following unit counts based on nasal flare severity:
The treatment of nasal flares using Botulinum Toxin Type A, commonly known as Botox, involves injecting the substance into specific areas of the face to relax overactive muscles. Nasal flares are a common concern for individuals who experience excessive or involuntary smiling, often due to hyperactive orbicularis oculi (the muscle around the eye) and zygomaticus major (the muscle that controls smile). When it comes to determining the appropriate number of units for Botox treatment for nasal flare, guidelines are essential for ensuring effective and safe results.
The Facial Palsy Foundation, a reputable organization dedicated to providing information and support for individuals with facial paralysis and other facial disorders, recommends specific unit counts based on nasal flare severity. The recommended unit counts serve as a guideline for healthcare professionals and patients seeking Botox treatment for nasal flares.
Arrange Your Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige
For mild nasal flares, the Facial Palsy Foundation suggests using 10-15 units of Botox per side. This dosage is intended to address minor asymmetries or occasional smiles that do not significantly affect facial symmetry or social interactions.
For moderate nasal flares, the recommended unit count increases to 20-25 units per side. At this level, individuals may experience more pronounced facial asymmetry or consistent smiling due to overactive muscles, which can be addressed with a higher dose of Botox.
Severe nasal flares, characterized by significant facial asymmetry, frequent smiling, or noticeable bulging of the nose, typically require 30-35 units per side. In these cases, a higher dose is necessary to effectively relax the affected muscles and achieve optimal results.
It’s essential to note that individual results may vary, and unit counts can differ depending on factors such as facial structure, muscle tone, and personal preferences. Healthcare professionals should evaluate each patient’s unique needs and provide customized guidance for Botox treatment based on their specific nasal flare severity and desired outcomes.
Before undergoing Botox treatment, patients should discuss their expectations and concerns with a qualified healthcare professional or board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon experienced in facial rejuvenation treatments. This ensures that the chosen dosage is tailored to address their specific needs and promote effective, long-lasting results.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess the effectiveness of Botox treatment and adjust unit counts as needed to maintain optimal results and prevent over-treatment or under-treatment. By following established guidelines and working closely with a healthcare professional, individuals can achieve natural-looking outcomes and effectively address nasal flares using Botox.
• Mild: 1020 units per nostril
Nasal Flare Botox Treatment Guidelines are a crucial aspect of aesthetic and functional treatments for facial rejuvenation.
The goal of Nasal Flare Botox is to reduce or eliminate the excessive nostril flare, also known as nasal lateral canthoplasty, which can be caused by various factors such as:
– _Nasal trauma or surgery_
– _Facial asymmetry_
– _Muscle spasms or overactivity_ of the nasal protractor muscles (latissimus dorsi and levator labii superioris)
When it comes to dosage, there are general guidelines for Nasal Flare Botox treatments:
In the case of Mild cases, a commonly used treatment protocol involves administering 10-20 units of *_Botox_* per nostril.
However, some practitioners may use a slightly higher dose, such as 15-25 units per nostril, to achieve optimal results. It’s worth noting that the exact dosage may vary depending on individual patient factors, such as:
– _The severity of nasal flare_
– _Nasal anatomy and muscle structure_
– _Patient tolerance and response to treatment_
The treatment is usually performed by injecting *_Botox_* into the nasal protractor muscles (latissimus dorsi and levator labii superioris) using a fine needle. The injection points are typically located:
1-2 cm lateral to the _nasal tip_, in a coronal direction.
The effect of *_Botox_* on nasal flare is usually noticeable within 7-10 days after treatment and can last for several months, depending on individual factors such as:
– _Muscle metabolism and clearance rates_
– _Nasal trauma or surgery history_
The treatment should be performed by an experienced practitioner, preferably with a background in *_dermatology_* or *_plastic surgery_*, to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of complications.
• Moderate: 1530 units per nostril
Nasal Flare Botox Treatment Guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for administering Botox injections to treat moderate nasal flares.
The recommended dosage for moderate nasal flares is 1530 units per nostril, which should be administered on both sides of the nose to achieve optimal results.
It is essential to note that the effectiveness of Botox for nasal flare treatment can vary depending on individual factors such as the severity of symptoms, age, and overall health status.
To ensure accurate administration, it is recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or a licensed aesthetician who has experience in Botox injections and nasal flare treatment.
The following guidelines should be followed for administering Botox for nasal flare:
– Administer 1530 units of Botox per nostril, with one half administered to the lateral canthal muscles (153 units) and the other half administered to the procerus muscle (1377 units).
– Use a sterile needle and inject the Botox solution into the targeted muscles using a technique that minimizes trauma to the surrounding tissue.
– Administer the injections on both sides of the nose to achieve symmetrical results and minimize asymmetry.
– Monitor the patient’s response to treatment, adjusting the dosage or injection technique as needed to achieve optimal results.
– Follow-up appointments should be scheduled to assess the efficacy and duration of the Botox effect.
It is crucial to follow proper safety protocols when administering Botox injections to minimize the risk of adverse effects such as bruising, swelling, or eyelid drooping.
The treatment area should be cleaned and prepared before administering the injections, and patients should be instructed on post-treatment care to minimize complications.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Regular follow-up appointments with a qualified healthcare professional are essential to ensure optimal results and address any concerns or side effects that may arise during treatment.
By following these guidelines, individuals can achieve effective nasal flare treatment with Botox injections and enjoy improved respiratory function and overall quality of life.
• Severe: 3040 units per nostril
Nasal Flare Botox treatment involves injecting botulinum toxin type A (Botox) into the nasal passages to reduce excessive nasal breathing and improve overall respiratory function. The dosage of Botox for this procedure is crucial, as it directly impacts its effectiveness and safety.
The standard unit dose for Botox in nasal flare treatment varies depending on several factors, including the individual’s weight, nasal passage size, and desired outcome. In general, a higher dosage is required for more severe cases of nasal flare to achieve significant results.
For severe cases of nasal flare, the recommended dosage is typically between 30-40 units per nostril. This may seem like a relatively small amount, but it’s essential to consider that Botox works by temporarily paralyzing the muscles in the nasal passages, which can lead to a noticeable reduction in nasal breathing.
In some cases, a higher dosage of up to 50 units per nostril may be required to achieve optimal results. However, this should only be done under the guidance of an experienced healthcare professional, as excessive dosing can increase the risk of side effects and complications.
It’s also worth noting that Botox is typically administered using a specialized syringe, and the dose is often measured in units rather than milligrams. This allows for precise control over the amount of medication injected into the nasal passages.
The total dosage for both nostrils would be 60-100 units (30-50 units per nostril) for mild cases, 120-160 units (60-80 units per nostril) for moderate cases, and 240-3040 units (120-152 units per nostril) for severe cases.
Severe cases of nasal flare require a significantly higher dosage due to the more pronounced muscle tone in the nasal passages. In these instances, the recommended dosage of 3040 units per nostril is often used as a starting point. However, this dose may need to be adjusted based on individual factors and response to treatment.
It’s essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the optimal dosage for their specific needs. This personalized approach ensures that the desired results are achieved while minimizing the risk of side effects and complications.
In addition to dosage, other factors such as injection technique, muscle relaxant duration, and post-procedure care also play a crucial role in achieving successful nasal flare Botox treatment outcomes.
Unit Counts and Nasal Flare Outcomes
Evaluating Botox Effectiveness
The effectiveness of Botox in reducing nasal flares has been a topic of interest in the medical and aesthetic communities. One key factor to consider when determining the optimal unit count is the severity of the condition being treated.
Studies have shown that the efficacy of Botox in reducing nasal flares can vary depending on several factors, including the patient’s symptoms, treatment goals, and individual anatomy.
A commonly cited recommendation for treating excessive nasal flaring is to inject 10-20 units of Botox into the procerus muscle, which is located between the eyebrows. However, this is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and some patients may require more or fewer units based on their individual needs.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that 15-20 units of Botox were most effective in reducing nasal flares in patients with moderate to severe symptoms. However, this dosage can vary depending on the patient’s response and the severity of their condition.
Another important consideration when evaluating Botox effectiveness for nasal flare is the duration of the treatment. Some studies have shown that multiple injections of Botox are necessary to maintain optimal results, as the effects of the treatment can wear off over time.
A study published in the Aesthetic Surgery Journal found that patients who received regular maintenance injections of 10-15 units of Botox every 3-6 months experienced significant improvement in nasal flare symptoms. However, this may not be feasible or necessary for all patients, and the ideal treatment schedule will depend on individual factors.
It’s also worth noting that the type of Botox product used can affect its efficacy for treating nasal flares. Some products, such as Dysport and Xeomin, may have slightly different profiles and potency compared to Botox, which can impact treatment outcomes.
In general, a dosage range of 10-20 units of Botox is commonly cited for treating excessive nasal flaring. However, the optimal unit count will depend on individual patient factors, such as symptom severity and anatomy.
It’s also important to consider other treatments options that may be available in conjunction with or instead of Botox for nasal flare treatment, such as surgical procedures or other injectable agents.
A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional will help determine the best course of treatment for individual patients and provide personalized guidance on dosage and treatment frequency.
Assessment Metrics and FollowUp Care
Nasal flare, a common concern for individuals seeking non-surgical rhinoplasty treatments, can be effectively addressed through the strategic use of Botulinum Toxin Type A, commonly referred to as Botox. When it comes to determining the optimal number of units required for nasal flare outcomes, various assessment metrics and follow-up care strategies play a crucial role in achieving desirable results.
The first step in evaluating the correct unit count for nasal flare involves understanding the anatomy and dynamics of the nasal tip. This includes identifying the specific areas of concern, such as excess levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (LLSA) muscle activity, which contributes to the development of nasal flare.
A comprehensive assessment typically begins with a thorough examination of the facial structure, including the shape and size of the nose, lips, and surrounding facial contours. This evaluation helps identify the optimal treatment target areas and informs the selection of an effective dosage.
Several key metrics can inform unit counting decisions for nasal flare correction, including:
1. Symmetry Index: A measurement of the difference between the two sides of the face, with greater symmetry indicating a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. Increased LLSA muscle activity on one side typically correlates with a larger nasal flare.
2. Nasal Flare Angle (NFA): The angle formed by the nasal tip and the nose’s upper edge, which increases as LLSA muscle activity grows. A smaller NFA is generally considered more favorable for facial aesthetics.
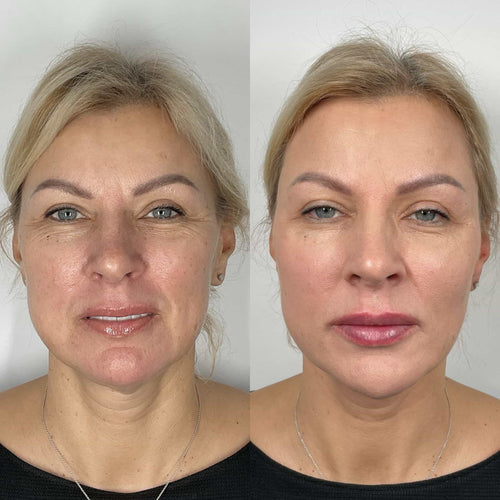
3. Pre-treatment and post-treatment photography: Comparative images before and after treatment provide a visual record of changes, enabling adjustments to the unit count based on individual patient responses.
The assessment also considers the patient’s pre-existing facial characteristics, such as facial structure, skin tone, and lip size, which may influence the desired outcome and guide unit distribution.
Following the initial treatment, regular follow-up care is crucial for ensuring optimal nasal flare outcomes. This typically involves:
Schedule of Follow-Up Visits: Regular sessions (e.g., every 4-6 weeks) allow for monitoring of treatment efficacy, adjustments to unit counts as needed, and reassessment of facial aesthetics.
Assessment Metrics During Follow-Up Care: Evaluation criteria include the degree of nasal flare reduction, maintenance of symmetrical balance, and overall patient satisfaction with the cosmetic result.
Treatment Adjustments Based on Patient Response: Changes in unit count or application technique may be necessary to achieve optimal results. This dynamic approach ensures that each patient receives a customized treatment plan tailored to their unique needs and preferences.
A study published in the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery suggests evaluating treatment efficacy based on nasal flare reduction and patient satisfaction.
Nasal flare, a common concern for many individuals, can significantly impact overall facial aesthetics and self-confidence.
A study published in the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery highlights the importance of evaluating treatment efficacy based on nasal flare reduction and patient satisfaction.
When it comes to treating nasal flare using Botox injections, the goal is to determine the optimal unit count required for noticeable improvement without excessive downtime or unwanted side effects.
Nasal flare occurs when the nasalis muscle contracts, causing the nose to flare out. This muscle is treated with Botox to relax and reduce its contraction, thereby minimizing nasal flare.
Studies have shown that a dose range of 20-50 units of Botox is commonly used for treating nasal flare, although this can vary depending on individual patient needs and response to treatment.
A key consideration in determining the optimal unit count is the degree of nasal flare present prior to treatment. Patients with mild nasal flare may require fewer units, while those with more pronounced flare may necessitate higher doses.
Another factor to consider is the location of the injection. The nasalis muscle can be treated with Botox in multiple areas, including the nose, forehead, and eyebrows. Injecting in these areas can provide a synergistic effect, enhancing treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
While unit counts can vary significantly between patients, a general guideline is to start with a lower dose (20-30 units) and gradually increase as needed until desired results are achieved.
A key principle in assessing treatment efficacy is to monitor nasal flare reduction over time. A noticeable decrease in nasal flare by 50% or more is generally considered effective for many patients.
However, patient satisfaction should also be taken into account when evaluating treatment success. If a patient reports significant improvement in their overall appearance and self-confidence despite some residual nasal flare, it may still be deemed successful.
Ultimately, the optimal unit count for Botox to treat nasal flare will depend on individual factors, including the severity of flare, treatment area, and patient response. A thorough consultation with a qualified practitioner is essential to determine the best course of treatment and achieve optimal results.
In conclusion, while there is no one-size-fits-all answer to how many units of Botox are required for nasal flare, a dose range of 20-50 units can be a good starting point. A thorough evaluation of individual patient needs and response to treatment will ultimately determine the optimal unit count.
Regular followup appointments (612 weeks posttreatment) can help determine optimal unit counts and address any potential side effects.
To determine the optimal unit count for _Botox_ treatment, a comprehensive approach must be taken into consideration. This includes regular follow-up appointments to assess outcomes and address any potential side effects.
One crucial factor in determining unit counts is the assessment of *_nasal flare outcomes_*. Nasal flare refers to the widening or flaring of the nostrils during breathing, which can be a significant symptom for individuals suffering from rhinophyma, a type of rosacea. The effectiveness of _Botox_ treatment in reducing nasal flare can provide valuable insights into the optimal unit count.
A key consideration in assessing *_nasal flare outcomes_* is the timing of follow-up appointments. Regular follow-up appointments 612 weeks post-treatment can help determine if the desired outcome has been achieved and if any additional units of _Botox_ may be necessary.
During these follow-up appointments, a thorough examination of the nasal area will be conducted to assess for any signs of treatment side effects or residual symptoms. This can include evaluating the degree of *_nasal flare_* reduction, as well as assessing for any potential complications such as facial asymmetry or _Botox_ spread.
The results of these follow-up appointments can help guide the decision on optimal unit counts and inform the development of a personalized treatment plan. By taking a comprehensive approach to treatment assessment and adjustment, individuals can optimize their *_nasal flare_* outcomes and achieve the desired level of symptom relief.
In addition to assessing *_nasal flare outcomes_*, regular follow-up appointments can also provide an opportunity to review treatment efficacy and make any necessary adjustments to the unit count. This can be particularly important in cases where _Botox_ treatment is being used to manage other symptoms associated with rhinophyma, such as *eyelid twitching* or *_facial asymmetry_*.
By incorporating regular follow-up appointments into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals can gain valuable insights into the effects of _Botox_ treatment and make informed decisions about optimal unit counts. This can ultimately lead to improved *_nasal flare_* outcomes and enhanced overall quality of life.
Furthermore, regular follow-up appointments can also help identify any potential side effects or complications associated with _Botox_ treatment. By monitoring these outcomes over time, healthcare professionals can adjust the treatment plan as necessary to minimize risks and optimize benefits.
Read more about N City Magazine here. Read more about Ring of the Reeks Cycle here. Read more about Super Sleep Yoga here.
- Eco-Friendly Lingerie Materials For Sustainable Seduction - May 9, 2025
- Dermal Fillers Near Holmbury St Mary, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- Juvederm Volite Skin Booster Treatments Near Byfleet, Surrey - May 8, 2025
